What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common dental problem that affects people of all ages. It is the result of the breakdown of the hard tissues of the tooth, caused by the buildup of bacteria in the mouth. Tooth decay can lead to cavities, which are holes in the teeth that can cause pain, sensitivity, and even infection if left untreated.
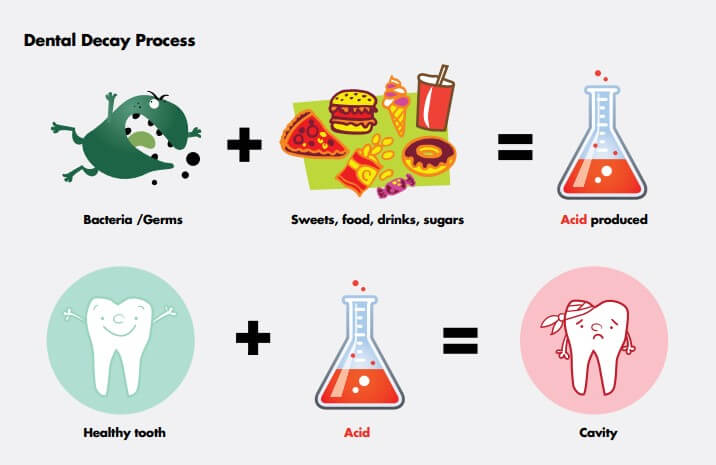
What Causes Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is caused by a combination of factors, including:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to the buildup of plaque on the teeth, which can eventually lead to tooth decay.
2. Sugary and Acidic Foods: Foods and drinks that are high in sugar and acid can cause tooth decay by eroding the enamel and exposing the softer, more vulnerable parts of the tooth.
3. Dry Mouth: A lack of saliva in the mouth can lead to tooth decay, as saliva helps to wash away food particles and neutralize acid.
What are the Symptoms of Tooth Decay?
The early stages of tooth decay may not cause any symptoms, which is why regular dental checkups are so important. However, as the decay progresses, you may experience:
1. Tooth Sensitivity: You may feel pain or sensitivity when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages.
2. Discoloration: You may notice dark spots or stains on your teeth.
3. Bad Breath: Tooth decay can cause bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth.
4. Pain: If the decay has reached the inner part of the tooth, you may experience pain or discomfort.
How can Tooth Decay be Prevented?
The good news is that tooth decay can be prevented with good oral hygiene and healthy habits. Here are some tips for preventing tooth decay:
1. Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your teeth twice a day and floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth and gums.
2. Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride helps to strengthen tooth enamel and protect against decay. Make sure your toothpaste contains fluoride.
3. Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods: Try to avoid or limit foods and drinks that are high in sugar and acid, such as soda, candy, and fruit juice.
4. Drink Plenty of Water: Drinking water helps to rinse away food particles and neutralize acid in the mouth.
5. Visit the Dentist Regularly: Regular dental checkups and cleanings are essential for preventing and detecting tooth decay.
FAQs:
Q: How does tooth decay happen?
A: Tooth decay happens when bacteria in the mouth produce acid that eats away at the enamel and dentin of the tooth. This can happen when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth.
Q: Is tooth decay contagious?
A: No, tooth decay is not contagious. However, the bacteria that cause tooth decay can be spread from person to person through saliva, so it’s important to practice good oral hygiene to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Q: Can tooth decay be reversed?
A: In the early stages, tooth decay can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and fluoride treatment. However, once a cavity has formed, it cannot be reversed and will require dental treatment.
Conclusion
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that can lead to cavities and other oral health issues. By practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding sugary and acidic foods, and visiting the dentist regularly, you can prevent tooth decay and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile. If you are experiencing any symptoms of tooth decay, be sure to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
References:
1. American Dental Association. (n.d.). Tooth decay.
2. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. (2018). Tooth decay.
3. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Tooth decay.
Related Links:
1. American Dental Association. (n.d.). Brushing your teeth.
2. American Dental Association. (n.d.). Flossing.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Water fluoridation.
4. American Dental Association. (n.d.). Diet and oral health.



